Spring5.x学习笔记1——工厂
引言
EJB(Enterprise Java Bean)存在的问题
- 运行环境苛刻
- 代码移植性差
总结:EJB 是重量级的框架。
什么是 Spring
Spring是⼀个轻量级的 JavaEE 解决⽅案,整合众多优秀的设计模式。
什么是轻量级?
- 对于运⾏环境是没有额外要求的;
开源:tomcat、resion、jetty
收费:weblogic、websphere
- 代码移植性⾼:不需要实现额外接⼝。
JavaEE 的解决方案:
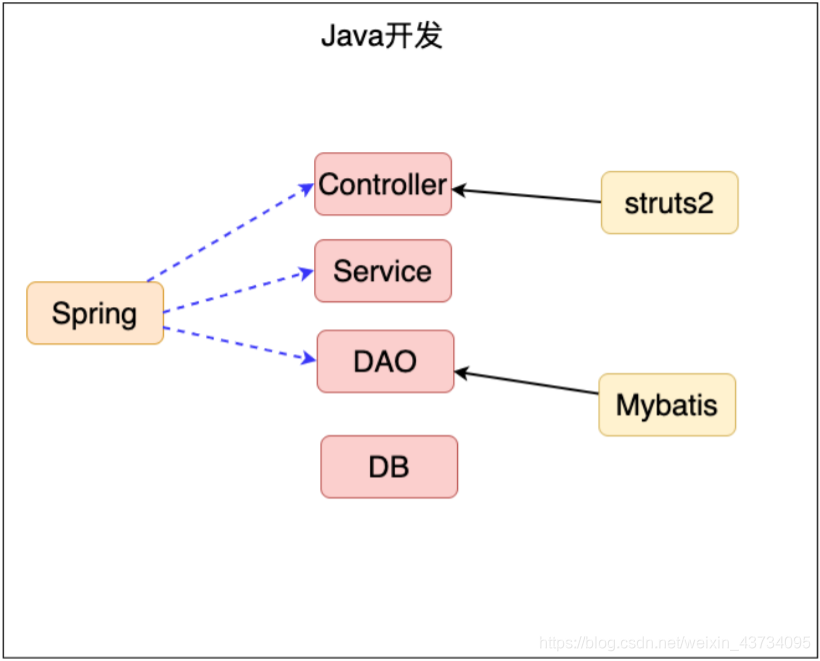
整合设计模式:
- 工厂
- 代理
- 模板
- 策略
工厂设计模式
设计模式
- 广义概念:面向对象设计中,解决特定问题的经典代码。
- 狭义概念:23种设计模式:工厂、适配器、装饰器、迭代器、代理、模板…
什么是工厂设计模式?
- 概念:通过工厂类,创建对象;
1
2
3
| User user = new User();
UserDAO userDAO = new UserDAOImpl();
12
|
- 好处:解耦合。
- 耦合:指定是代码间的强关联关系,一个类的改变会影响到另另一个类;
问题:不利于代码维护;
简单:把接⼝的实现类,硬编码在程序中;
1
| UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
|
简单的工厂设计
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| package com.baizhiedu.basic;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class BeanFactory {
private static Properties env = new Properties();
static{
try {
InputStream inputStream = BeanFactory.class.getResourceAsStream("/applicationContext.properties");
env.load(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static UserService getUserService() {
UserService userService = null;
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(env.getProperty("userService"));
userService = (UserService) clazz.newInstance();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return userService;
}
public static UserDAO getUserDAO(){
UserDAO userDAO = null;
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(env.getProperty("userDAO"));
userDAO = (UserDAO) clazz.newInstance();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return userDAO;
}
}
|
配置文件applicationContext.properties:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
userService = com.baizhiedu.basic.UserServiceImpl
userDAO = com.baizhiedu.basic.UserDAOImpl
|
通用的工厂设计
问题:简单工厂会存在大量的代码冗余。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| package com.baizhiedu.basic;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class BeanFactory {
private static Properties env = new Properties();
static{
try {
InputStream inputStream = BeanFactory.class.getResourceAsStream("/applicationContext.properties");
env.load(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Object getBean(String key){
Object ret = null;
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(env.getProperty(key));
ret = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ret;
}
}
|
使用方式:
- 定义类型 (类)
- 通过配置文件的配置告知工厂
applicationContext.properties 中 key = value;
- 通过工厂获得类的对象
Object ret = BeanFactory.getBean("key");
第一个Spring程序
环境搭建
依赖查询网站:https://mvnrepository.com/;
配置 Spring 的 jar 包:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
|
Spring的配置文件
- 配置文件的放置位置:任意位置,没有硬性要求;
- 配置文件的命名 :没有硬性要求,建议:applicationContext.xml;
Spring核心API
ApplicationContext
- 作用:Spring 提供的
ApplicationContext 这个工厂,用于对象的创建;
好处:解耦合
ApplicationContext 是接⼝类型;
接⼝:屏蔽实现的差异
非web环境 (main junit) :ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
web环境 :XmlWebApplicationContext
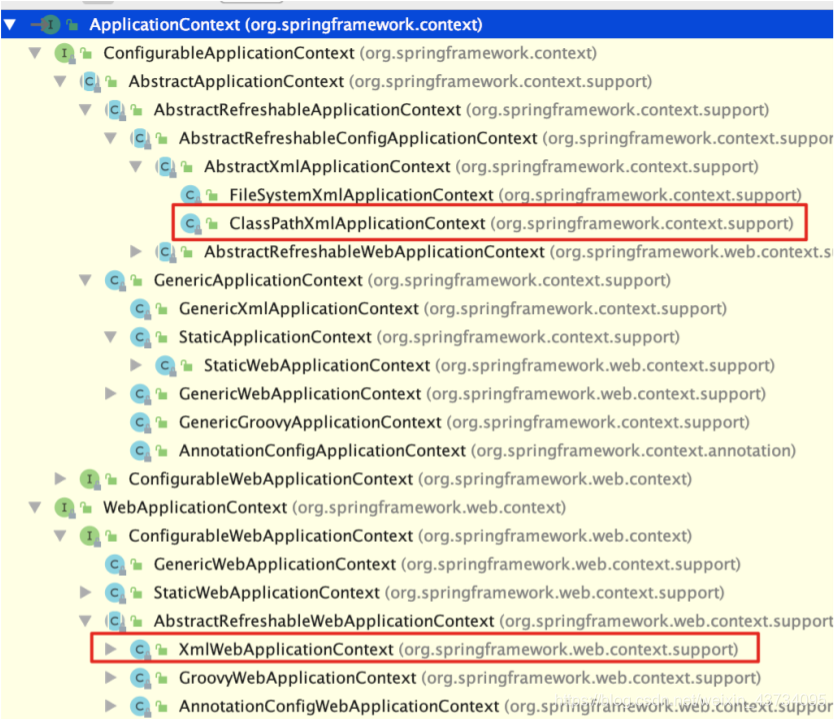
- 重量级资源:
ApplicationContext 工厂的对象占JVM大量内存。
不会频繁的创建对象 ,一个应用只会创建一个工厂对象。
ApplicationContext 是一个重量级的共享资源,即是线程安全的(多线程并发访问)。
程序开发
- 创建类型:Person.java
- 配置文件的配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.yusael.basic.Person"/>
</beans>
|
- 通过工厂类,获得对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@Test
public void test() {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person)ctx.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
|
细节分析
名词解释:Spring ⼯⼚创建的对象,叫做 bean 或者 组件(componet);
Spring 工厂的相关的方法
getBean:传入 id值 和 类名 获取对象,不需要强制类型转换。
1
2
3
4
|
Person person = ctx.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
123
|
getBean:只指定类名,Spring 的配置文件中只能有一个 bean 是这个类型。
1
2
3
4
|
Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
123
|
getBeanDefinitionNames:获取 Spring 配置文件中所有的 bean 标签的 id 值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println("beanDefinitionName = " + beanDefinitionName);
}
12345
|
getBeanNamesForType:根据类型获得 Spring 配置文件中对应的 id 值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
String[] beanNamesForType = ctx.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (String id : beanNamesForType) {
System.out.println("id = " + id);
}
12345
|
containsBeanDefinition:用于判断是否存在指定 id 值的 bean,不能判断 name 值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
if (ctx.containsBeanDefinition("person")) {
System.out.println(true);
} else {
System.out.println(false);
}
123456
|
containsBean:用于判断是否存在指定 id 值的 bean,也可以判断 name 值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
if (ctx.containsBean("p")) {
System.out.println(true);
} else {
System.out.println(false);
}
123456
|
配置文件中的细节
如果 bean 只配置 class 属性:
1
2
| <bean class="com.yusael.basic.Person"></bean>
1
|
- 会自动生成一个 id,
com.yusael.basic.Person#1
可以使用 getBeanNamesForType 验证。
- 应⽤场景:
如果这个 bean 只需要使⽤⼀次,那么就可以省略 id 值;
如果这个 bean 会使⽤多次,或者被其他 bean 引⽤则需要设置 id 值;
name 属性:
- 作⽤:⽤于在 Spring 的配置⽂件中,为 bean 对象定义别名(小名)
- name 与 id 的相同点:
ctx.getBean("id") 或 ctx.getBean("name") 都可以创建对象;、<bean id="person" class="Person"/> 与 <bean name="person" class="Person"/> 等效;
- name 与 id 的区别:
- 别名可以定义多个,但是 id 属性只能有⼀个值;
- XML 的 id 属性的值,命名要求:必须以字⺟开头,可以包含 字⺟、数字、下划线、连字符;不能以特殊字符开头
/person;
XML 的 name 属性的值,命名没有要求,/person 可以。
但其实 XML 发展到了今天:ID属性的限制已经不存在,/person也可以。
Spring工厂的底层实现原理(简易版)

思考
问题:未来在开发过程中,是不是所有的对象,都会交给 Spring ⼯⼚来创建呢?
回答:理论上是的,但是有特例 :实体对象(entity) 是不会交给Spring创建,它由持久层框架进⾏创建。
Spring5.x与日志框架的整合
Spring 与日志框架进行整合,日志框架就可以在控制台中,输出Spring框架运行过程中的某些重要的信息。
好处:便于了解Spring框架的运⾏过程,利于程序的调试。
默认日志框架
Spring 1.x、2.x、3.x 早期都是基于commonslogging.jar
Spring 5.x 默认整合的⽇志框架 logback、log4j2
Spring 如何整合日志框架?
Spring5.x 整合 log4j:
- 引进
log4j.jar 包;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
|
- 引进
log4.properties 配置文件;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
log4j.rootLogger = debug,console
log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.Target=System.out
log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
|
学习资料:B站孙帅


